The two building materials that are most frequently utilized in construction are cement and concrete. Despite the fact that they are commonly used interchangeably, the terminology is different. The completed product used in structures, concrete, has cement as one of its ingredients.
The distinctions between cement and concrete must be understood by anybody working in the construction sector since they have an impact on the final product’s strength, affordability, and durability. The definitions of cement and concrete, as well as the numerous types, production processes, applications, advantages, and related misconceptions, will all be covered in this piece.
The meaning of Cement
A popular binding substance used in buildings is cement. It is a fine powder created by heating and grinding a combination of limestone, clay, and other minerals into a fine powder. When combined with water, the cement hardens and binds things together to create a sturdy and long-lasting building.
Types of Cement

Different types of cement are available in the market, each with unique properties and uses. Some of the commonly used types of cement include:
- Portland Cement: It is the most widely used cement type for general construction purposes. It is a fine powder from limestone, clay, and other minerals.
- White Cement: This type of cement is used for architectural purposes and is known for its bright white color.
- Rapid Hardening Cement: As the name suggests, this type of cement hardens quickly and is used when a fast setting is required, such as in precast concrete structures.
- Pozzolanic Cement: This type of cement is made by mixing Portland cement with pozzolanic materials such as volcanic ash, fly ash, or silica fume.
Cement Manufacturing Process
Several steps are involved in the cement manufacturing process, including:
- Mining: Quarries provide raw minerals such as limestone and clay.
- Crushing and grinding: Once the raw materials have been mined, they are crushed and ground into a fine powder.
- Mixing: The basic powdered components are blended in a specified ratio to create a homogeneous combination.
- Heating: The mixture is heated to a high temperature in a kiln to generate clinker.
- Cement is made by grinding the clinker into a fine powder.
Applications of Cement
- Construction of buildings, bridges, and roads
- Manufacturing of precast concrete products such as pipes, poles, and panels
- Stabilization of soil and improvement of its bearing capacity
- Making mortars and grouts for fixing tiles, bricks, and stones
- Production of cement-based materials such as concrete blocks, pavers, and tiles.
Advantages of Cement
- Strong and long-lasting cement can bear enormous weight and great pressure.
- It is reasonably priced and easily accessible on the market.
- Excellent fire-resistant qualities are present in cement.
- Because it is simple to combine and use, it is frequently chosen for construction.
Disadvantages of Cement
- Cement production requires a lot of energy, which increases greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cement manufacturing pollutes the environment and is bad for people’s health.
- Due to its rigidity, cement is prone to cracking and shrinking.
- Because cement uses a lot of water, it can be problematic in areas with limited water supplies.
The Meaning of Concrete
Concrete is a flexible building material comprising cement, water, aggregates (such as sand, gravel, or crushed stone), and occasionally additives. These substances combine to create a tough, sturdy material that can be molded into many forms and sizes.
Types of Concrete

For diverse building projects, numerous kinds of concrete are employed. Among the varieties of concrete that are often utilized are:
The most popular concrete form is normal-strength concrete, with a compressive strength of 20 to 40 MPa.
Great-rise buildings, bridges, and other structures requiring great strength are built with high-strength concrete with a compressive strength of around 50 to 90 MPa.
Lightweight Concrete: As the name suggests, this type of concrete is lighter in weight than normal concrete and is used in the construction of buildings where weight is a concern.
Self-Compacting Concrete: This type of concrete is highly fluid and can be easily poured into molds without vibration. It is used in the construction of precast concrete structures.
Manufacturing Process of Concrete
The manufacturing process of concrete involves several steps, including:
- Mixing: The cement, water, aggregates, and additives are mixed in a specific ratio using a concrete mixer.
- Transporting: Once the mixture is ready, it is transported to the construction site using trucks or other transportation means.
- Placing: The mixture is then poured into molds or formwork, where it can set and harden.
- Curing: The concrete is then cured for a specific period to attain maximum strength and durability.
Applications of Concrete
- Manufacturing of precast concrete products such as pipes, poles, and panels
- Stabilization of soil and improvement of its bearing capacity
- Making of floors, walls, and roofs in buildings
- Production of concrete-based materials such as blocks, pavers, and tiles.
Advantages of Concrete
- Concrete is a strong and durable material that can withstand heavy loads and harsh weather conditions.
- It is fire-resistant and provides excellent insulation.
- It is relatively inexpensive and readily available in the market.
- Concrete is a versatile material that can be molded into various shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages of Concrete
- The manufacturing process of concrete is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Concrete has a high water demand, which can be a concern in areas with water scarcity.
- It is a brittle material and is prone to cracking and shrinkage.
- Concrete is a heavy material, which can make transportation and handling difficult.
Key Differences between Cement and Concrete
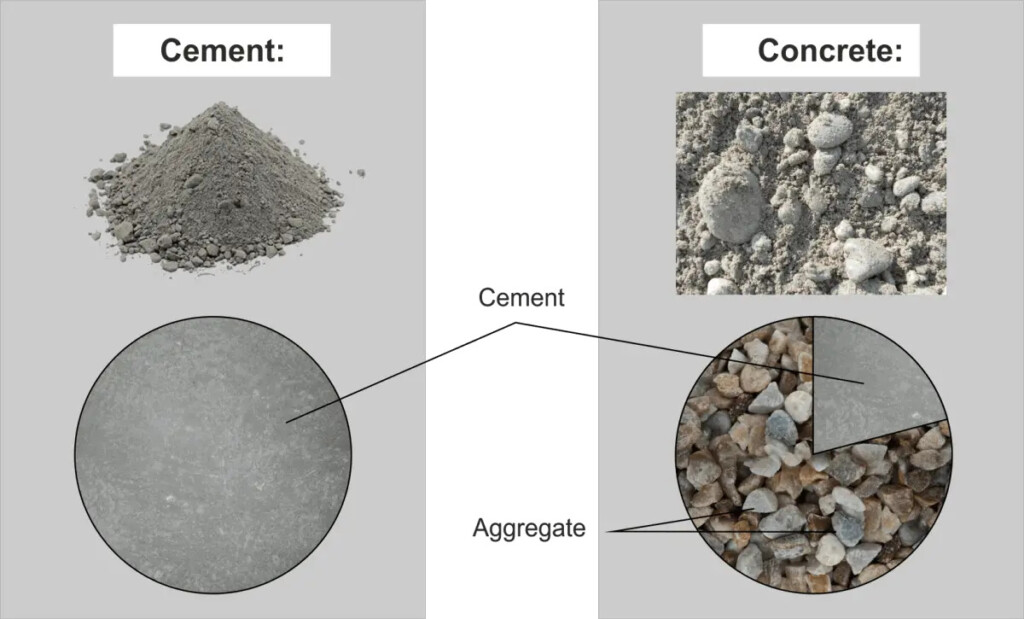
Although cement and concrete are often used interchangeably, they are different. Cement is an ingredient used in concrete production, while concrete is the final product used in construction. Some of the key differences between cement and concrete are:
Composition: Cement comprises mainly limestone and clay, while concrete comprises cement, water, aggregates, and sometimes additives.
Strength: Cement is a binder that holds together the other materials in concrete, but it does not provide strength on its own. Concrete, on the other hand, is a strong and durable material that can withstand heavy loads and harsh weather conditions.
Application: Cement is used in various applications, including producing concrete, mortar, and grout. Concrete is used to construct buildings, bridges, roads, and other structures.
Importance of Using the Right Cement in Concrete
The type of cement used in the production of concrete can have a significant impact on the strength and durability of the final product. It is essential to use the right type of cement for the intended application to ensure the best results.
For example, using high-strength cement to produce concrete used in a residential building may not be necessary and can result in unnecessary costs. On the other hand, using low-strength cement in constructing a bridge or a high-rise building can compromise the structure’s structural integrity.
Common Misconceptions about Cement and Concrete
There are several misconceptions about cement and concrete, some of which include:
- Cement and concrete are the same: As mentioned earlier, cement and concrete are different. Cement is an ingredient used in the production of concrete.
- Concrete is a permanent material: While concrete is durable and long-lasting, it is not permanent. Harsh weather conditions, heavy loads, and other factors can damage it over time.
- All cement is the same: Different types of cement are used for various applications. Using the wrong type of cement can result in a weak and unstable structure.
- Concrete sets and hardens due to drying: Concrete does not set and harden due to drying. It is a chemical process when the cement reacts with water to form a hardened material.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cement and concrete are vital building materials, and comprehension of their distinctions is crucial. To get the greatest results, it is crucial to utilize the proper type of cement for the application. Cement is a component used in the manufacture of concrete.
Concrete and cement come in various forms, each having special qualities, benefits, and drawbacks. Even if there are some widespread misunderstandings regarding cement and concrete, being informed may assist in guaranteeing the security, toughness, and affordability of building projects. For building projects, picking the correct materials might be the difference between success and failure.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between cement and concrete?
Cement is an ingredient used in concrete production, while concrete is the final product used in construction. Cement comprises mainly limestone and clay, while concrete consists of cement, water, aggregates, and sometimes additives.
-
What are the different types of cement and their applications?
The most common types of cement include ordinary Portland cement, slag cement, fly ash cement, and white cement. The type of cement used depends on the intended application, such as high-strength cement for the construction of bridges or low-heat cement for mass concrete structures.
-
What are the advantages of using concrete in construction?
Concrete is a strong and durable material that can withstand heavy loads and harsh weather conditions. It is also relatively inexpensive, fire-resistant, and can be molded into various shapes and sizes, making it ideal for construction projects.
-
How is concrete manufactured?
Concrete is manufactured by mixing cement, water, aggregates, and sometimes, additives. The mixture is then poured into molds or forms, where it hardens and sets to form the final product.
-
What are the common misconceptions about cement and concrete?
Some common misconceptions about cement and concrete include the belief that they are the same thing, that all cement is the same, that concrete is a permanent material, and that concrete sets and hardens due to drying. Understanding the facts can help ensure that construction projects are safe, durable, and cost-effective.